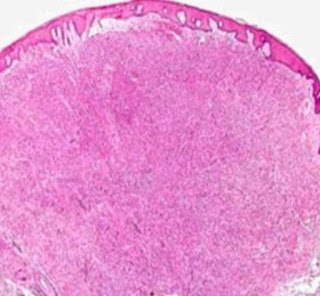
Answer of Dermatopathology Case 110
Dermatofibroma with Monster Cells Visit: Dermatopathology Site Visit: Pathology of Dermatofibroma Abstracts: Giant dermatofibroma with monster cells.Am J Dermatopathol. 2002 Feb;24(1):36-8. We report a case of a 64-year-old woman with a giant dermatofibroma on her back with the unusual histologic feature of monster cells. The firm, exophytic, 3-cm nodule had purple and yellow components with surface telangiectasia. Histologic examination demonstrated characteristic findings of a dermatofibroma, including rete ridge flattening and bridging; a stroma containing scattered, large, round, eosinophilic collagen bundles; and a polymorphous dermal infiltrate of spindle and xanthomatous cells with scattered siderophages. Some xanthomatous cells demonstrated features consistent with monster cells, including huge bizarre nuclei and one or more nucleoli. Immunohistochemical staining for factor XIIIa was positive. A diagnosis of giant dermatofibroma with monster cells (DFMC) was made. Giant dermato