Answer of Dermatopathology Case 50
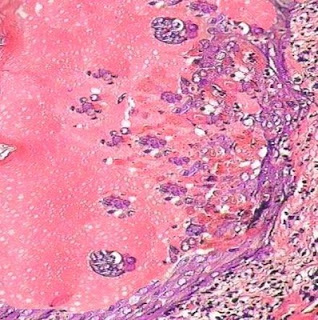
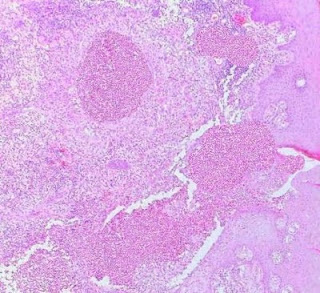
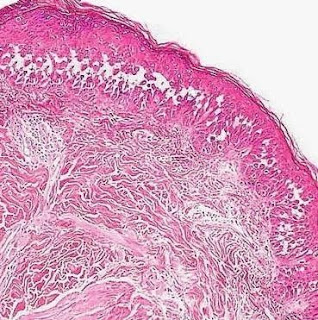
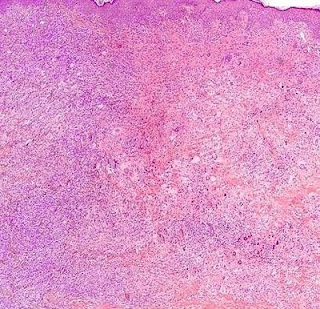
Cutaneous Herpes Simplex Infection Visit: Dermatopathology site Visit: Herpes Simplex Infection Abstract: Histopathology of the more common viral skin infections. Actas Dermosifiliogr .2010 Apr;101(3):201-16. We describe the histopathological characteristics of viral skin infections. Herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus produce an intraepidermal vesicle with variable degrees of epithelial necrosis. Typical findings include keratinocytes with ballooned nuclei with a ground-glass appearance and giant multinucleated keratinocytes. In the endothelial cells of the dermal blood vessels, cytomegalovirus produces large eosinophilic nuclear inclusions surrounded by a clear halo. Human herpes virus 8 is etiologically associated with Kaposi sarcoma. In its early stages, this tumor contains blood vessels with a fine endothelium passing through the dermal collagen bundles. In the plaque and nodular stages, the vessel lumens are more clearly visible and there is a progressive increase in...