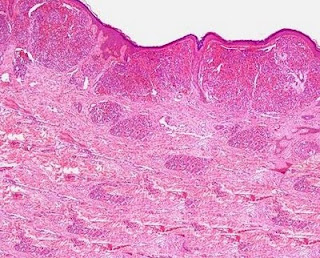
Answer of Dermatopathology Case 52
Acquired Tufted Angioma Visit: Dermatopathology site Visit: Pathology of Acquired Tufted Angioma Abstract: Perianal acquired tufted angioma associated with pregnancy: case report. Tech Coloproctol. 2002 Sep;6(2):117-9. Tufted angiomas are rare lesions described as slowly growing/spreading erythematous macules especially located in the upper trunk and neck. Herein we report the case of perianal location of a tufted angioma in a young pregnant woman. She came to our observation complaining of perianal pain accompanied by bleeding at defecation. A lesion resembling a perianal fissure was observed. Mild hypertonia of the internal sphincter was confirmed at manometry. After one week of ineffective medical treatment, surgery was planed at the end of the sixteenth week under local anaesthesia. The lesion was excised and a minimal sphincterotomy was performed; histopathology report described features of a tufted angioma. The pregnancy proceeded regularly, without anal symptoms, followed by nor