Answer of Dermatopathology Case 108
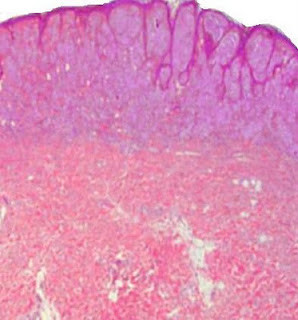
Median Raphe Cyst Visit: Dermatopathology Site Visit: Pathology of Median Raphe Cyst Abstract: Median raphe cyst of the penis.Dermatol Online J. 2005 Dec 1;11(3):37. Cysts of the median raphe are uncommon. We describe a 43-year-old man with an asymptomatic nodule on the glans penis. Excision of the lesion was performed followed by histological and immunohistochemical studies. Histopathological examination revealed a solitary unilocular cystic cavity in the corium, lined by a pseudostratified columnar epithelium, among which mucinous cells where identified. Hints of decapitation secretion occurred at the apex of the luminal layer. An immunohistochemical study using a standard avidin-biotin peroxidase method disclosed CK7 and CK13 reactivity in the columnar cells. Epithelial membrane antigen (EMA) and carcinoembryonic (CEA) antigen immunoreactivity occurred at the apical border of the luminal cells. No staining was obtained with anti-CK20, human milk fat globulin 1 (HMFG1) and anti- S10